Reverse Osmosis (RO)
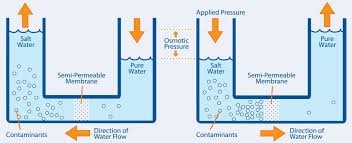
Reverse Osmosis is a membrane separation process in which a Solvent ( Water ) is forced to a region of low soluble concentration from high concentration region through a semi permeable membrane by applying Pressure that is greater than osmotic pressure. The Membrane acts as a barrier to the flow of solute (dissolved solids) molecules, there by separating Solute from Solvent.
The RO Process in general used for desalination of water. Saline Water is passed through the Membrane module under Pressure, higher than the osmotic pressure of Saline Water. Relatively clean water, called Permeate, passes through the membrane and comes out of the low-pressure side. Salts are retained in the residual water on the high pressure side, thereby being concentrated.
Unlike other desalting processes, Reverse Osmosis is not an energy intensive process. The only energy supplied is to the pump motors.
Unlike other desalting processes, Reverse Osmosis is not an energy intensive process. The only energy supplied is to the pump motors.
- Flat Sheet
- Tubular
- Hollow Fine Fibre
- Cellulose Acetate
- Aromatic Polyamide
Pre Treatment of Feed Stream plays Vitol role in smooth functioning of RO Plant. The performance of a system depends on factors such as membrane type, flow control, feed water quality, temperature and pressure.The pre-treatment methods have been divided into two broad categories (i) Pre-treatment to prevent chemical damage to the membrane (ii) Pre-treatment to prevent fouling.In general, Feed streams are treated for following purposes
Feed streams are treated for following purposes |
Different types of Fouling |
|---|---|
| To remove Turbidity and Suspended Solids | Membrane scaling |
| To adjust and control the Ph and temperature of the feed | Fouling by metal oxides |
| To inhibit or control the formation of compounds, which when precipitated will plug the water passage or coat the membranes | Device plugging |
| To disinfect and prevent slime growths or prevent contaminant of the equipment | Colloidal fouling |
| To remove emulsified and unemulsified oil or similar organics | Biological fouling |